Fabrication know-how
Discover know-how/tips/cautions shared by aligner fabricating experts
It explains how to make devices using 3D printers.
Printing process
Slicing > 3D printing > Post processing (For DLP/SLA printers only)
Select printer
DLP/SLA or FDM type printer can be selected according to user environment or purpose.
* Minimum specification: 100㎛ or less for X/Y/Z-axis resolution
DLP/SLA type | FDM type | ||
 | Type of curing resin with light |  | Type of laminating by melting filaments |
  | Sophisticated output: SLA > DLP Printing speed: SLA < DLP Maintenance: SLA < DLP Strength 1. Fast printing 2. The printout surface is smooth 3. It can manufacture much smaller and more precise prints than FDM type Weakness 1. It is difficult to make large prints due to brightness or distortion by wide light 2. Weak print strength 3. Short product life 4. Sensitive to temperature. Deformation occurs at room temperature over 60℃ 5. Expensive equipment and materials |   | Strength 1. Popular 2. Cheap equipment and materials 3. Long product life 4. Strong print strength 5. Convenient post-processing Weakness 1. Slow printing 2. The printout surface is rough and not precise |
Preparation
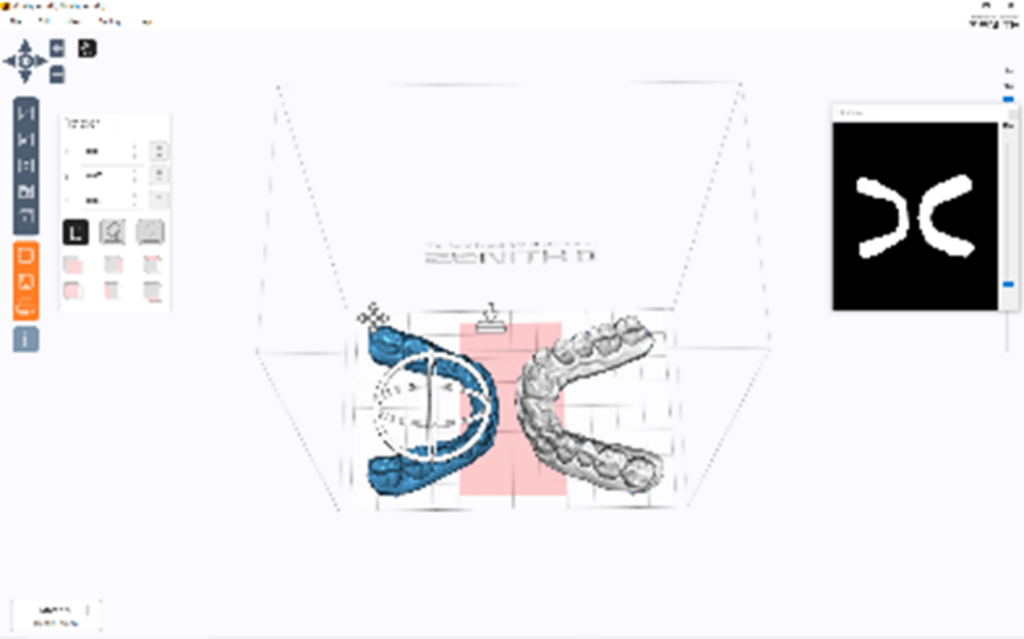
Slicing program settings and check points by equipment
By adjusting the Z-axis of slicing program, lightly bury the model or us a floor aid to prevent print failure.
Check points to avoid printing failure
DLP/SLA type | FDM type |
Check floor temperature Check for foreign objects The resin should be well mixed  | Check floor temperature Check filament twisting Check for nozzle clogging  |
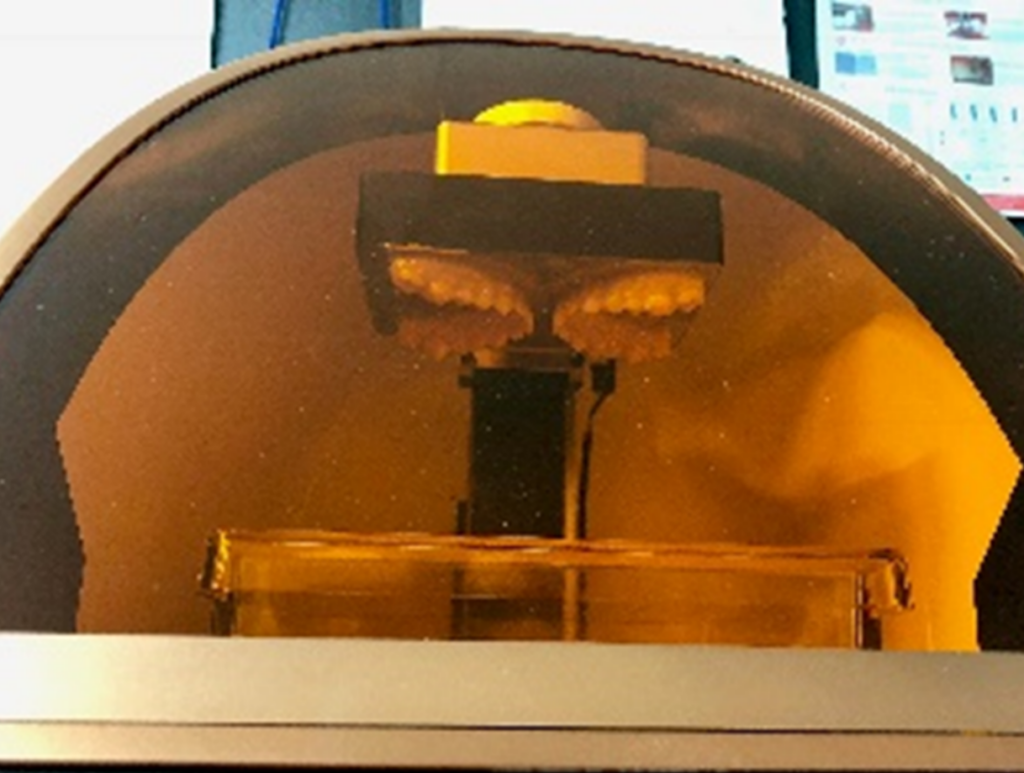
Printing
DLP/SLA type
FDM type
Post-processing
This is a job only for DLP/SLA printers, there is a process of removing excess resin remaining on the printout and curing.
Put the printout in a barrel filled with alcohol, remove excess resin with a fine-bristle toothbrush. Put the dried printouts into the curing equipment.